That which is in red was updated after input from Dr. Winterson...See below for her input.
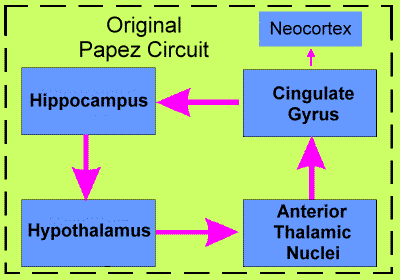
Papez believed that the experience of emotion was primarily determined by the cingulate cortex and, secondly, by other cortical areas. Emotional expression was thought to be governed by the hypothalamus. The cingulate gyrus projects to the hippocampus, and the hippocampus projects to the hypothalamus by way of the bundle of axons called fornix. Hypothalamic impulses reach the cortex via relay in the anterior thalamic nuclei.

Cingulate Gyrus
Located on medial surface of the brain
Principal fiber bundle connecting the two cerebral
hemispheres
Coordinates pleasant memories of previous emotions
Participates in the emotional reaction to pain
Participates in the regulation of aggressive behavior
Deals with feeling states (affect)
Hippocampus
Located adjacent to olfactory cortex in the temporal lobe
Involved consolidation of short term memory to long-term
factual or declarative memory
Suppresses rage response
The emotional aspects are more to aid the process of establishing the
linkages
example, an emotional charged memory is more readily
established and retrieved than one not colored by emotion, however the
emotion is not necessarily specific to the event.
Hypothalamus
Important output center of the limbic system
Controls most vegetative & endocrine functions
Controls many aspects of emotional behavior
Deals with the expression of emotion
Programmed response
Anterior Thalamic Nuclei
Gateway to the cerebral cortex
Computes the specific emotional response
modulation of
emotional feelings or affect
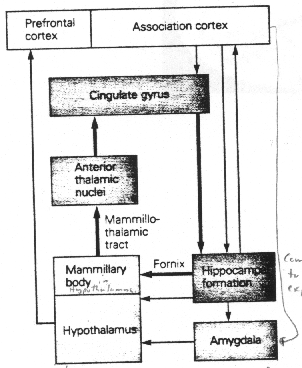
Modern Papez Circuit
Modern belief is that there is more "interplay" between the original 4 areas as well as addition of more areas and pathways (see above graphic). This provides for a more complex, fine-tuned emotional response.
Pathways Added To Circuit
Bi-directional communication between the hippocampus and
the association cortex
Allows for
comparison of old information and current stimulus
Example
"What you are think you are seeing really isn't scary at all"
Blunts
behavior response
Input from the hypothalamus to the prefrontal cortex
Executive decision
making
Influences emotional response
"Pick Your Battles"
New Structures Added To Circuit
Amygdala
Located deep inside temporal lobe
Many bi-directional connections to
hippocampus, hypothalamus, thalamus, cortex
Projects current status in relation
to both surroundings and thoughts
The center for ID'ing danger
(fundamental for self preservation)
Involved in Fear conditioning
Processes behavioral response
Critical in long term memory
"Window of the limbic
system"
An important component of the learning is the emotion.
| The comments in this box are from Dr.
Winterson. They have been integrated into the essay outline above
and highlited in red. "The hippocampus can be better characterized as being involved in the consolidation of short term to long term factual or declarative memory. The emotional aspects are more to aid the process of establishing the linkages. So for example, an emotional charged memory is more readily established and retrieved than one not colored by emotion, however the emotion is not necessarily specific to the event. On the other hand, the amygdala is more involved with "fear conditioning" per se. An important component of the learning is the emotion. I may have led you astray in the first lecture trying to convince you that emotions are important to learning. Under anterior nucleus, since this nucleus projects to the cingulate gyrus its most immediate effects would likely be the modulation of emotional feelings or affect (not expression which implies some type of behavior). Finally, you may want to add something about parts of the hypothalamus outside of the mammillary bodies." |
Last Updated 09/06/01 08:53:36 PM
Return To The MNA2001 Homepage